System Design
Resources
- System Design Interview An Insider’s Guide by Alex Xu
- Notes on Alex Xu Book
- System Design Primer
- Grokking the System Design Interview github notes
- drawing tool escalidraw
- TechLead overview
- Blog on System Design topics, one of its articles was liked by William (IMO best competitor)
Strategy prep
- read this notes
- Anki notes and questions (you have an app)
- System Design Primer github repo
- System Design Interview insider book
Tackle the problem by doing it just like you would at work.
A 4-step process for effective system design interview:
1. Understand the problem and establish design scope
Goal: Gather requirements and clarify assumptions. WRITE THEM DOWN. Never start start designing before understanding requirements.
Example questions: Product question -> technical question
DESIGN QUESTIONS
Feature/Functional requirements
- What are the required features for the system? -> Main functionalities?
- Who are my clients (external, internal, quants, mobile, web, international)?
- How are they going to use it? -> What services clients want to run? (determine API-s functions)
- Have we built this service before, or I am building it for the first time?
- What do we want to optimize with our design -> Determine logging metrics
Non-functional requirements
- How many users are there? -> Horizontal vs Vertical Scalability
- Whats the traffic volume, DAU? -> Single Server setup or MultiServer Setup?
- Internal or External or Global system? -> Do we need high availability?
- Available or Consistent data storage? -> Determine tradeoff in CAP theorem
- How fast do we want to answer requests? -> Latency vs Consistency?
- How many requests per second do we expect?
- What is the scale of the system? Is it built for a startup or a big company with a large user base? -> Scalability?
- Scale of the system such as requests per second (RPS), requests types, data written per second, data read per second)
- Automatic scaling? The addition/deletion of servers should be automatic based on traffic?
DATA QUESTIONS
- What are the I/O of the system? Data Flow
- Data Volumes(if need horizontal scaling use consistent hashing)
- What type of data would I need to store? Just text, or images videos? Static Dynamic content?
- What is the expected read to write ratio, read or write oriented.? (Master-Master, or Master-Slave database)
- If we need to horizontally scale do we have evenly distributed data? Celebrity problem?
- How long we need to keep the data?
- If we do historical loads how much back in time should they be?
- What's the distribution of accessing data? Is a long tail one (suitable for caching popular content).
- Do we need to our data store to be agile? Change and process in real time?
- On-prem or in the cloud?
- What are my endpoints of different parts what APIs would I need?
Implementation questions
- Building from scratch? Can we use Third-Party API-s.
- Can we leverage some of the existing cloud infrastructures provided by Amazon, Google, or Microsoft?
2. Propose high-level design and engage interviewer
Goal: Propose blueprint of initial design. Ask for feedback.
"Does that seem like a sensible strategy?"
Tasks:
- Do back-of-the-envelope calculations to evaluate if your blueprint fits the scale constraints Commonly asked back-of-the-envelope estimations: QPS, peak QPS, storage, cache, number of servers QPS = queries per second. 1 day ~ 80,000 seconds
- Draw box diagrams with key components (Clients (user) mobile/web), APIs, web servers, data stores, cache, CDN, message queue.
3. Design deep dive Once you agree with your interviewer on the blueprint, go into details on each component. Design the most critical components first. This part is specific to the interview and interviewer.
4. Wrap up Interviewer asks follow up questions. Or you can do some further discussion. Topics:
- Monitoring your solution (analytics to decide whether the solution is good).
- Performance optimization - e.g do we need multi data center setup using clouod provider
- Identify system bottlenecks and discuss potential improvements
- Recap your design
- Error cases (server failure, network loss, etc.) are interesting to talk about.
- Operation issues are worth mentioning. How do you monitor metrics and error logs?
- Scale the design - load balancer, horizontal scaling, caching, database sharding
- Discuss trade-offs:
Performance vs scalability
Latency vs throughput
Availability vs consistency
General tips
- gather requirement and write them down (don't be afraid to ask stupid questions)
- start with simplest possible setup (single server, single database, single storage)
- iterate, improve crucial parts (database (sharding,replication); storage(AWS S3, replicated buckets); load balancer)
- make improvements on more important parts first (database usually goes down before server)
Horizontal scaling improvements
CCARRF
- loose consistency
- loose complexity
- win availability
- win reliability
- win redundancy
- win failover (no SPOF)
Buzz words
horizontal, vertical scaling, availability, failover, reliability, redundancy, consistency, maintainability, load balancer, message queue, asynchronism, workers, data streaming services, database partitioning (split incoming data into different databases based on data rule e.g a-n, n-z), database replication (master-slaves, master-master), sharding, synchronization, parallel computing, SHA code, cache, CDN, Availability Zones (Data Centers), SQL = relational, NoSQL = non relational databases, celebrity problem (in data bases), reads >> writes usually (use cache), volatile memory = temporary memory, memcache (caching SQL) = @cache (Private) in python, MongoDB = document database, DynamoDB = key-value store, stateless vs stateful web tier, user session data, VPS(Virtual Private Server) = your own ubunto (EC2 instance) vs shared hosts, hypervisors, sharded database (shards), normalized and de-normalized databases, high cohesion low coupling (scale independently), single point of failure SPOF, Disk slower than In-memory database slower than In-memory cache, ACID properties of a relational database, Transaction, CAP theorem, PACELC theorem (high availability=data replication -> tradeoff between consistency and latency) BLOB (binary large object), BLOB cache, TTL, weak/eventual/strong consistency, cache-aside, cache write-through, cache-write-through, cache-write-back, cache-refresh-ahead, distributed system, multi-server setup, micro-services, database transaction, begin->select-> commit/rollback
Youtube
When looking for host providers:
- FTP vs SFTP (secured file transfer protocol)
- VPS (virtual private server) vs shared hosts(many users use same server)
- VPS are your EC2 instances in AWS (your own ubunto) safe from other users but still susceptible to the provider
- VPS uses hypervisors. A hypervisor, also known as a virtual machine monitor or VMM, is software that creates and runs virtual machines (VMs).
Load balancer strategies to balance:
- based on work load, least busy servers take the work
- dedicated servers for specific jobs (html server, Python server etc.)
- job i is taken by server i % N (problem might not have uniformly distributed workload)
Load balancer problem? Single Point of Failure.
- buy 2 load balancers (pretty expensive 100k)
RAID technology is a virtualization of data memory - data many disks put into "one" and keep copy/backups to be safe.
Stateless architecture to have easier horizontal scaling on the web tier. Keep session data in NoSQL/SQL database shared by all servers (SPOF), better replicate it.
MySQL caches queries, the same query running more than once is cached. memcache is like @cache (Private) in Python
Database replication - Master-Master, Master Slaves
Database partitioning - partition incoming data using some rule (a-n, n-z) and split into different databases
Load balancing help to distribute traffic to many different servers. Helps scalability, latency, throughput.
NGINX is a load balancing software service. Can do DNS load balancing. Make the DNS returns you different ip addresses for same domain distributing to different servers.
Throughput is a measure of how many units of information a system can process in a given amount of time.
Caching - e.b often you'd hitting the database (reads) you need to setup cache. Cache services Memcached, Redis, Cassandra
CDN-s store static data, global network which caches your content.
In interview might be asked to design a database schema:
- what are the primary keys
- what are your indecies
Indecies in a database make it fast - no need to do linear search in WHERE clause, indecing gives you random access. Indexing your table improves the joins - nee to index the column on which you join.
Database optimizations:
- replication (master slaves)
- indexing
Scaling stuff:
- Webservers - use load balancers to do horizontal scaling
- Image server - CDN, cache
- Database server - cache, replication (solves reads)
- Database server writes - Sharding
Sharding your database (database partitioning) - horizontal (split rows) and vertical (split different columns) sharding Each shard goes to different server.
You don't want to scale too early and put optimization in the begining.
Clement System Design interview example
Databases
Differences between SQL and NoSQL
Storage
- SQL: store data in tables.
- NoSQL: have different data storage models.
Schema
- SQL
- Each record conforms to a fixed schema.
- Schema can be altered, but it requires modifying the whole database.
- NoSQL:
- Schemas are dynamic.
Querying
- SQL
- Use SQL (structured query language) for defining and manipulating the data.
- NoSQL
- Queries are focused on a collection of documents.
- UnQL (unstructured query language).
- Different databases have different syntax.
Scalability
- SQL
- Vertically scalable (by increasing the horsepower: memory, CPU, etc) and expensive.
- Horizontally scalable (across multiple servers); but it can be challenging and time-consuming.
- NoSQL
- Horizontablly scalable (by adding more servers) and cheap.
ACID
- Atomicity, consistency, isolation, durability
- SQL
- ACID compliant
- Data reliability
- Gurantee of transactions
- NoSQL
- Most sacrifice ACID compliance for performance and scalability.
Which one to use?
SQL
- Ensure ACID compliance.
- Reduce anomalies.
- Protect database integrity.
- Data is structured and unchanging.
NoSQL
- Data has little or no structure.
- Make the most of cloud computing and storage.
- Cloud-based storage requires data to be easily spread across multiple servers to scale up.
- Rapid development.
- Frequent updates to the data structure.
Reasons for SQL:
- Structured data
- Strict schema
- Relational data
- Need for complex joins
- Transactions
- Clear patterns for scaling
- More established: developers, community, code, tools, etc
- Lookups by index are very fast
Reasons for NoSQL:
- Semi-structured data
- Dynamic or flexible schema
- Non-relational data
- No need for complex joins
- Store many TB (or PB) of data
- Very data intensive workload
- Very high throughput for IOPS
Common types of NoSQL
Key-value stores
- Array of key-value pairs. The "key" is an attribute name.
- Redis, Vodemort, Dynamo.
Document databases
- KeyValue, but values are documents.
- Documents are grouped in collections.
- Each document can have an entirely different structure.
- CouchDB, MongoDB , Dynamo
Wide-column / columnar databases
- Column families - containers for rows.
- No need to know all the columns up front.
- Each row can have different number of columns.
- Cassandra, HBase.
Graph database
- Data is stored in graph structures
- Nodes: entities
- Properties: information about the entities
- Lines: connections between the entities
- Neo4J, InfiniteGraph
System Design Interview - An Insider Guide
Chapter 1 - Scale from zero to million users
This chapter discusses the process of scaling from a single web server to an architecture with: User, DNS, CDN, Load Balancer, Web tier (Stateless servers), Data Tier (Sharded Databases + Replication), Cache, NoSQL database to keep user session data (stateless servers), message queue, logging and metric tools, Data Centers for international coverage.
• Keep web tier stateless \ • Build redundancy at every tier \ • Cache data as much as you can \ • Support multiple data centers \ • Host static assets in CDN \ • Scale your data tier by sharding \ • Split tiers into individual services \ • Monitor your system and use automation tools
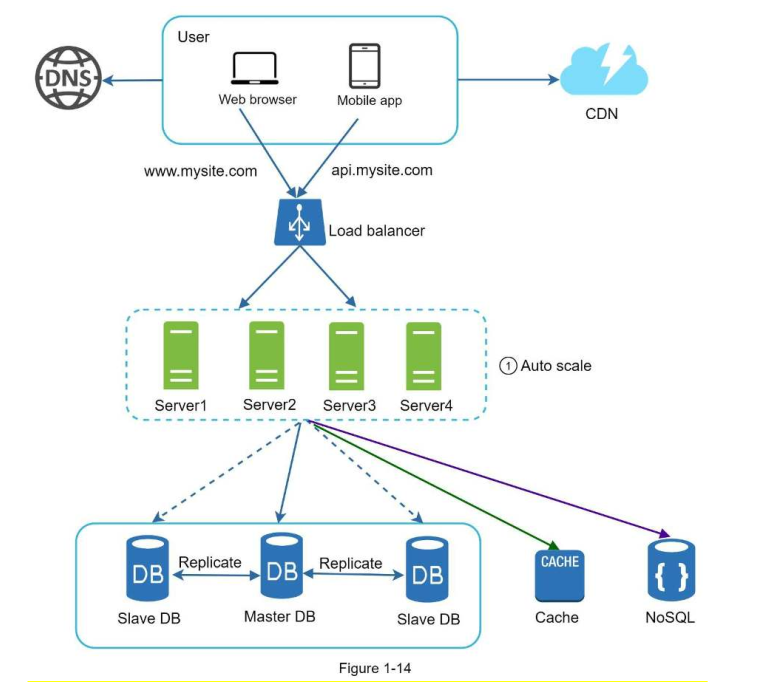
System Design : https://bit.ly/41PTaAp
Winning System Design Case Studies: https://tinyurl.com/yfvyrjn7
Github : https://shorturl.at/hlow0
ML System Design Series : https://rb.gy/dd8dfe
Design Google Drive : https://bit.ly/3uXdQZ7
Design Messenger App : https://bit.ly/3DoAAXi
Design Instagram : https://bit.ly/3BFeHlh
Design Twitter : https://bit.ly/3qIG9Ih
Design Robinhood : https://bit.ly/3BFeHlh
Design Swiggy: https://bit.ly/3BFeHlh
Design CashApp : https://bit.ly/3BFeHlh
Design Kayak: https://bit.ly/3DoAAXi
Design Paytm : https://bit.ly/3qIG9Ih
Design ESPN Streaming : https://bit.ly/3qIG9Ih
Design Agoda : https://bit.ly/3xP078x
Design Razorpay : https://bit.ly/3xP078x
Design Apple Music : https://bit.ly/3xP078x
Design CricHD: https://bit.ly/3xP078x
Design Alibaba: https://bit.ly/3xP078x
Design Substack: https://bit.ly/3xP078x
Design TrueCaller: https://shorturl.at/pzABN
Design Stock exchange Design System: https://shorturl.at/svCK1
Design Distributed Cache : https://shorturl.at/fjBV6
Design Twilio : https://shorturl.at/uDJP7
Design Google Docs : https://tinyurl.com/mr4d9v83
Design Doordash : https://tinyurl.com/27nh5s7s
Design MS Docs : https://tinyurl.com/9fpa8jpc
Design Zomato : https://tinyurl.com/566t34ph
Design Linkedin : https://bit.ly/3OjXy7c
Design Google Maps : https://bit.ly/3BDdTwn
Design Telegram : https://bit.ly/42N5LW2
Design Snapchat : https://bit.ly/3pRP3pW
Design One Drive : https://bit.ly/438bAwZ
Design Quora : https://bit.ly/3FeD9dL
Design Tinder : https://bit.ly/3Mcyj3X
Design TikTok : https://bit.ly/3UUlKxP
Design Netflix : https://bit.ly/3GrAUG1
Design Uber : https://bit.ly/3fyvnlT
Design Youtube : https://bit.ly/3dFyvvy
Design Reddit : https://bit.ly/3OgGJrL
Design Facebook’s Newsfeed : https://bit.ly/3RldaW7
Design Amazon Prime Video : https://bit.ly/3hVpWP4
Design Dropbox : https://bit.ly/3SnhncU
Design Yelp: https://bit.ly/3E7IgO5
Design Whatspp : https://bit.ly/3M2GOhP
Backlinks